What is Air Conditioning and What Services Are Available for It?
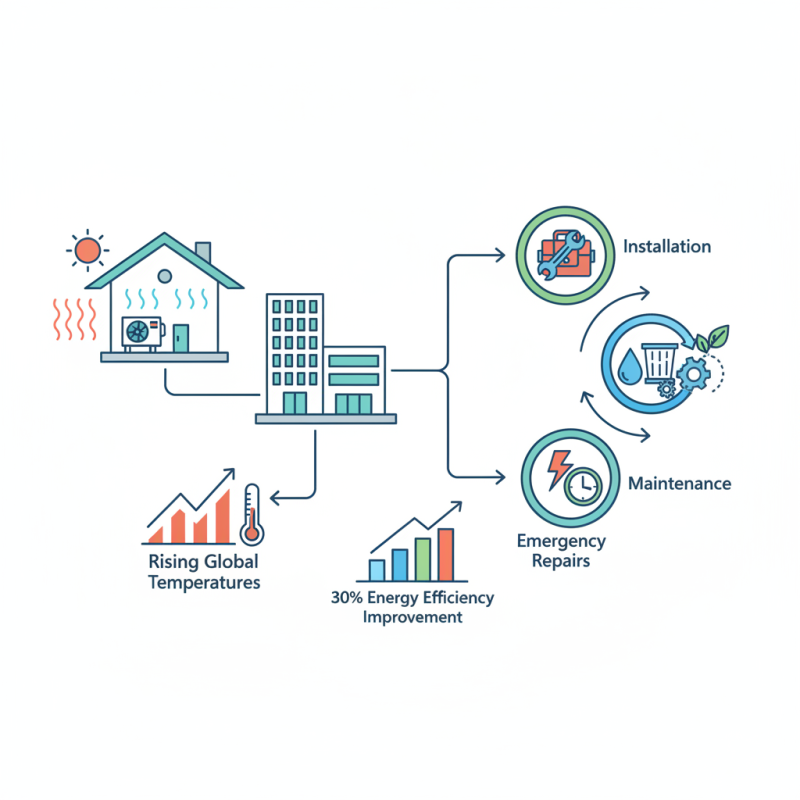
Air conditioning plays a crucial role in enhancing indoor comfort across various environments, ranging from residential homes to commercial spaces. With climate change leading to rising global temperatures, the demand for efficient air conditioning systems has surged. According to the International Energy Agency, air conditioning accounts for roughly 10% of global electricity consumption, and this figure is expected to rise as more regions experience extreme heat. As such, understanding the different types of air conditioning systems and the associated services air conditioning provides is essential for consumers aiming to optimize their indoor conditions.
In addition to climate comfort, air conditioning systems greatly influence energy efficiency and indoor air quality. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that well-designed and maintained air conditioning systems can improve energy efficiency by up to 30%. Regular maintenance services, such as cleaning filters and ensuring proper refrigerant levels, are critical for system longevity and optimal performance. As the market evolves, various services air conditioning professionals offer, from installation to ongoing maintenance and emergency repairs, become increasingly important in ensuring that these systems operate at peak efficiency and reliability, contributing to a sustainable and comfortable living environment.
Definition and Overview of Air Conditioning Systems
Air conditioning (AC) systems play a vital role in regulating indoor environments by controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality. An air conditioning system typically consists of a refrigerant cycle, a compressor, evaporator and condenser coils, and an air handling unit. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, about 90% of new homes built in the United States include air conditioning, highlighting its significance in modern living. The efficiency of these systems can be reflected in their Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), with newer models achieving ratings above 16, compared to older systems often falling below 10. This improvement not only reduces energy consumption but also contributes to lower utility bills.
In terms of services related to air conditioning, routine maintenance and timely repairs are crucial for optimal system performance. According to a study by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA), regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of air conditioning units by up to 30%. Common services include comprehensive inspections, filter replacements, and refrigerant checks, which collectively enhance energy efficiency and indoor air quality. Moreover, the increasing trend toward smart home integration has prompted the development of advanced control systems, allowing for more precise temperature management and energy usage tracking. As HVAC technology evolves, these services are adapting, ensuring that air conditioning systems remain efficient and effective in meeting the changing needs of consumers.
Types of Air Conditioning Systems and Their Applications
Air conditioning systems come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. Primarily, there are
central air conditioning systems, ductless mini-split systems, window units, and portable air conditioners.
Central systems are ideal for larger spaces, providing efficient cooling throughout multiple rooms via a network of ducts.
According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, approximately 87% of American homes use some form of air conditioning,
highlighting the importance of these systems for comfort and efficiency.
 Ductless mini-split systems offer flexibility, especially in older homes where ductwork installation is impractical.
These systems consist of an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor units,
allowing for targeted cooling that can save energy costs. The global air conditioning market is expected to reach
$155 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient systems and the growing trend of smart technology integration in HVAC systems.
Additionally, window and portable air conditioners serve as effective solutions for smaller spaces or for those who need temporary cooling.
As environmental regulations tighten, the push towards eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient models is set to reshape the landscape of air conditioning technology,
underscoring the diverse applications and advancements in this essential industry.
Ductless mini-split systems offer flexibility, especially in older homes where ductwork installation is impractical.
These systems consist of an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor units,
allowing for targeted cooling that can save energy costs. The global air conditioning market is expected to reach
$155 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient systems and the growing trend of smart technology integration in HVAC systems.
Additionally, window and portable air conditioners serve as effective solutions for smaller spaces or for those who need temporary cooling.
As environmental regulations tighten, the push towards eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient models is set to reshape the landscape of air conditioning technology,
underscoring the diverse applications and advancements in this essential industry.
Key Components and Functionality of Air Conditioning Units
Air conditioning (AC) is an essential system designed to regulate indoor temperature, humidity, and air quality, contributing significantly to comfort and health. At the core of any AC unit lies several key components that work in tandem to achieve desired environmental conditions. These include the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, properly maintained air conditioning systems can operate at about 15% more efficiency, highlighting the importance of understanding these components for effective service delivery.
The compressor, often referred to as the heart of the AC system, plays a crucial role in circulating refrigerant throughout the unit. The condenser releases heat absorbed from the interior, while the evaporator absorbs heat, facilitating a cooling effect. The expansion valve regulates refrigerant flow within the system, allowing for optimal pressure and temperature levels. A study by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America reveals that approximately 60% of maintenance issues stem from improper installation and lack of regular upkeep. This emphasizes the need for regular professional services, including routine check-ups and system cleanings, to ensure optimal functioning and longevity of the air conditioning units.
Air Conditioning Unit Components and Their Efficiency Ratings
Common Maintenance Services for Air Conditioning Systems
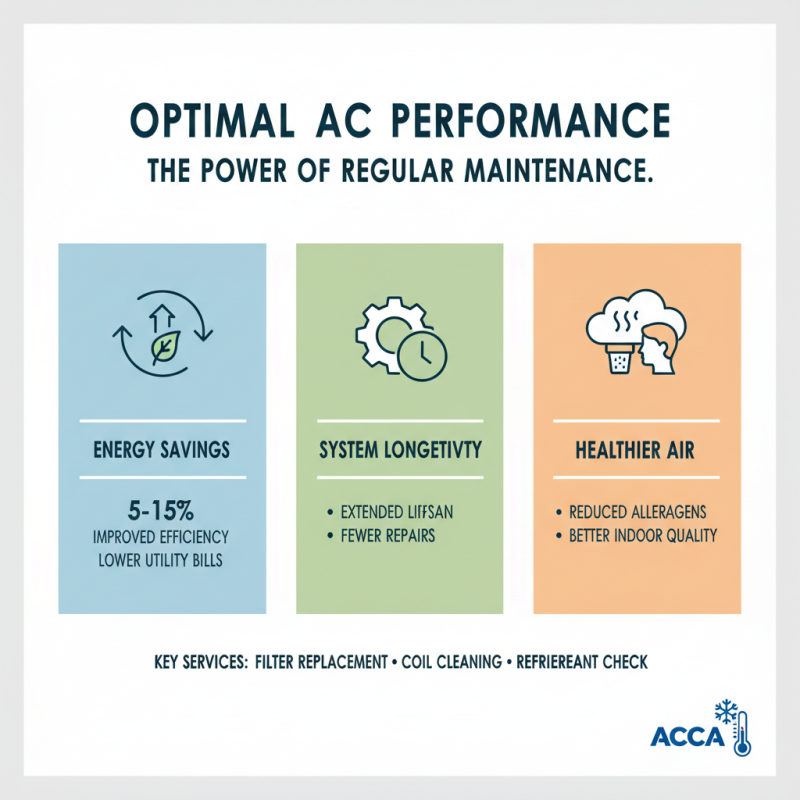
Regular maintenance of air conditioning systems is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. According to the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA), proper maintenance can improve system efficiency by 5-15%. This can lead to significant energy savings, especially during peak cooling seasons when demand is high. Common maintenance services include checking and replacing air filters, inspecting refrigerant levels, and cleaning the evaporator and condenser coils. These tasks not only enhance efficiency but also contribute to better indoor air quality by reducing allergens and pollutants.
Another important aspect of air conditioning maintenance is the thermostat calibration and ductwork inspection. The U.S. Department of Energy emphasizes that improperly calibrated thermostats can cause a system to operate inefficiently, increasing energy consumption by up to 10%. Additionally, leaky ducts can significantly reduce cooling efficiency, with studies suggesting that poorly sealed ducts can lose 20-30% of the conditioned air before it reaches living spaces. Regular inspections and tune-ups by qualified technicians can mitigate these issues, ensuring that air conditioning systems run smoothly and effectively throughout their lifespan.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations in Air Conditioning
Air conditioning plays a significant role in providing comfort in residential and commercial spaces, but it's essential to consider its energy efficiency and environmental impact. With growing concerns about climate change, the air conditioning industry is making strides to enhance the efficiency of cooling systems. Modern units are designed to use less energy, reducing the carbon footprint associated with temperature regulation. Features like variable speed compressors and smart thermostats allow for more precise control of indoor climates, which can lead to significant energy savings.
Tips for maximizing your air conditioner's energy efficiency include regularly maintaining your system by changing filters and scheduling professional inspections. Keeping windows and doors sealed can prevent cool air from escaping and reduce the workload on your unit. Also, consider using programmable thermostats to adjust the temperature when you're not home, further decreasing unnecessary energy usage.
When investing in air conditioning systems, consider environmentally friendly refrigerants and technologies that contribute less to global warming. Energy Star-rated units are designed to consume less electricity, and when paired with renewable energy sources, they can significantly minimize environmental impact. Prioritizing energy-efficient models not only conserves energy but can also lead to lower utility bills in the long run.
Related Posts
-

What is a Home Air Conditioning System and How Does It Work
-
10 Essential Tips for Choosing and Installing Air Conditioning Systems
-

How to Choose the Right Residential Air Conditioning Installation for Your Home Comfort Needs
-

2023 Guide to Air Conditioning Systems: Understanding SEER Ratings and Energy Efficiency for Your Home
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Residential Air Conditioning System for Your Home
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Home Air Conditioning System for Your Needs